AP Chemistry
Unit 1: Atomic Structure and Properties
Unit 1: Atomic Structure and Properties
Standards
1.1 Moles and Molar Mass
1.2 Mass Spectroscopy of Elements
1.3 Elemental Composition of Pure Samples
1.4 Composition of Mixtures
1.5 Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration
1.6 Photoelectron Spectroscopy (PES)
1.7 Periodic Trends: Ionization Energy, Atomic/Ionic Radii, Electron Affinity, Electronegativity
1.8 Valence Electrons and Ionic Compounds
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
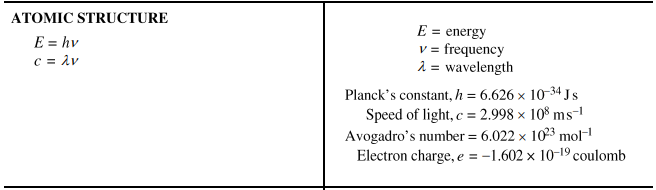
1.1 Equation: n = m/M
1.5 Coulomb's Law
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
1.2 Interpreting Mass Spectra of samples containing multiple elements or peaks arising from species other than singly charged monatomic ions will not be assessed on the AP Exam.
1.5 Assigning Quantum Numbers
1.7 Electron configurations of elements that are exceptions to the Aufbau Principle will not be assessed.
Resources
AP Chem YouTube Review Unit 1 - 1.1-1.4 Moles, Mass Spec, Elemental Composition, and Mixtures (46 min)
AP Chem YouTube Review Unit 1 - 1.5-1.8 Atomic Structure, Electron Config, Spectroscopy, Periodic Trends (51 min)
Interpreting PES Data: A few videos, a handout, a slideshow, and other links to assist in interpreting Photoelectron Spectroscopy data.
Stoichiometry: Videos tutorials explaining stoichiometric conversions (mass/moles/particles/volume), limiting reactants, and percent yield.
Periodic Table & Trends: Atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and other trends found on the periodic table.
Electron Orbital Diagrams: Discusses how to draw orbital diagrams and introduces basic principles including Aufbau, Pauli Exclusion, and Hund's Rule.
Significant Figures & Rounding Significantly: Discusses several examples with a thorough explanation on sig figs.
Paramagnetic vs Diamagnetic (5 mins)
Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties
Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties
Standards
2.1 Types of Chemical Bonds
2.2 Intramolecular Force and Potential Energy
2.3 Structure of Ionic Solids
2.4 Structure of Metals and Alloys (Substitutional and Interstitial)
2.5 Lewis Diagrams
2.6 Resonance and Formal Charge
2.7 VSEPR and Bond Hybridization
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
2.7 Molecular geometry, bond angles, relative bond energies based on bond order, relative bond lengths, presence of dipole moments, hybridization of valence orbitals (sp 180°, sp2 120°, sp3 109.5°)
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
2.3 Knowledge of specific types of crystal structures will not be assessed on the AP Exam.
2.7 Derivation and depiction of hybrid orbitals will not be assessed; although sigma and pi bonding, VSEPR shapes, and the types of hybrid orbitals will be assessed as mentioned above.
2.7 Hybridization involving d-orbitals will not be assessed.
2.7 Molecular Orbital Theory will not be assessed.
Resources
AP Chem YouTube Review Unit 2 - 2.1-2.4 Chemical Bonds, Intramolecular Force, and Structure of Solids (__ min)
AP Chem YouTube Review Unit 2 - 2.5-2.7 Lewis Diagrams, Formal Charge, and VSEPR (__ min)
VSEPR and Molecular Geometry: A video overview of how to use Lewis Dot Diagrams to determine the shape of molecules.
Sigma vs. Pi Bonds (3 min)
Sigma vs. Pi Bonds 2 (9 min)
Animation of Quantum Model (1 min)
Unit 3: Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Unit 3: Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Standards
3.1 Intermolecular Forces
3.2 Properties of Solids
3.3 Solids, Liquids, and Gases
3.4 Ideal Gas Law
3.5 Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT)
3.6 Deviation from Ideal Gas Law
3.7 Solutions and Mixtures
3.8 Representations of Solutions
3.9 Separation of Solutions and Mixtures Chromatography
3.10 Solubility
3.11 Spectroscopy and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
3.12 Photoelectric Effect
3.13 Beer-Lambert Law
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
3.1 Be able to identify the IMFs (hydrogen bonds, dipole forces, London dispersion forces) present by using molecular polarities and molecular geometries (linear, bent, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, tetrahedral, etc.).
3.11 Microwave radiation (transitions in molecular rotations levels); Infrared radiation (transitions in molecular vibrational levels); Ultraviolet/Visible radiation (transitions in electronic energy levels)
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
3.3 Phase diagrams will not be assessed
3.8 Colligative properties will not be assessed
3.8 Calculations of molality, percent by mass, and percent by volume will not be assessed
Resources
Photoelectric Effect: A PhET simulation that allows students to see how the intensity and frequency/energy of light can eject electrons from a metal plate resulting in an electric current.
Ideal Gas Law: Practice Problems Explained
Ideal Gas Law with Density: Practice Problems Explained
Avogadro's Law: Video explanation of how Avogadro's Law is applicable.
Combined Gas Law: Includes derivations for Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac.
Which Gas Law Do I Use? A great video explaining how to choose the right formula to use with word problems.
Solutions Overview: Includes molarity, dilutions, and other topics regarding concentration.
Calculating Concentration: molarity, molality, mass fraction, ppm, ppb
Introduction/Review of Intermolecular Forces: Includes hydrogen bonding, dipole forces, and London dispersion forces
Ionic Bonds and Coulomb's Law: (Khan Academy) Explains how forces of attraction varies based on intermolecular attractions and the distance between particles.
More on Intermolecular Forces (with quiz): (Professor Dave) Explains intermolecular forces in a different way and provides a quiz and answers at the end of the video.
Unit Summary: Summarizes entire unit and coincides with an AP textbook (Chemistry: The Central Science by Brown, LeMay, et. al., 11th Edition).
Comparison of Inter/Intra-molecular Forces: (Khan Academy article)
Bozeman Science Videos on Intermolecular Forces:

Unit 4: Chemical Reactions
Unit 4: Chemical Reactions
Standards
4.1 Intro to Reactions
4.2 Net Ionic Equations
4.3 Representations of Reactions
4.4 Physical and Chemical Changes
4.5 Stoichiometry
4.6 Intro to Titrations
4.7 Types of Chemical Reactions
4.8 Intro to Acid-Base Reactions
4.9 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
4.1 Indicators of chemical reaction (heat/light, formation of a gas, precipitation, color change)
4.2 Write and balance net ionic equations
4.3 Balance (molecular and complete ionic) chemical equations
4.5 Stoichiometry calculations involving ideal gas law and molarity
4.6 Identify the following in a titration: titrant, analyte, equivalence point, end point
4.7 The following ions are "always soluble": sodium, potassium, ammonium, nitrate
4.8 Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases (proton donor/acceptor)
4.9 Balance redox reactions using half-reactions
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
4.7 Identifying or using the terms "reducing agent" or "oxidizing agent" will not be assessed
4.7 Memorization of "solubility rules" besides the four primary ions (sodium, potassium, ammonium, nitrate)
4.8 Lewis definition of acids and bases will not be assessed
Resources
How to Use the Activity Series: A short video on how metals replace other metals based on the activity series.
A Trick for Memorizing the Activity Series: A mnemonic is shown at the end of the video that will allow you to memorize the metals in the activity series chart.
Writing Total and Net Ionic Equations: An example using a precipitation reaction.
Solubility Rules and Precipitation Reactions: Several video examples of using solubility rules to identify precipitates and then writing net ionic equations.
Oxidation Numbers: How to assign oxidation numbers
Oxidation Number Calculator: Use this tool when you can't figure out individual oxidation numbers
RedOx Reactions: Identifying oxidation and reduction half-reactions, using oxidation numbers, and writing balanced net ionic equations for redox reactions.
Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics
Standards
9.7 Galvanic (Voltaic) and Electrolytic Cells
9.8 Cell Potential and Free Energy
9.9 Cell Potential Under Nonstandard Conditions
9.10 Electrolysis and Faraday's Law
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
9.3 Table: G, H, S for favorability
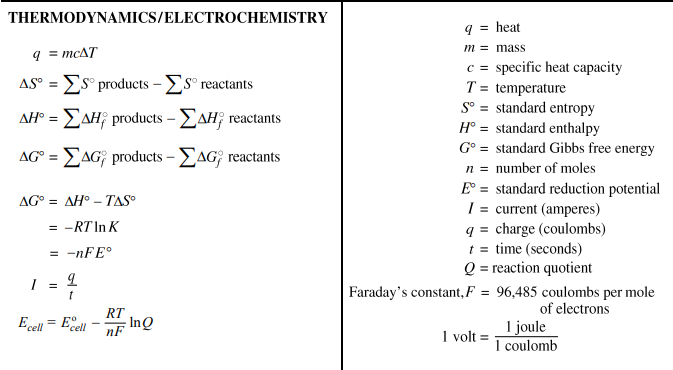
9.9 Qualitative use of the Nernst equation: E = E° - (RT/nF) ln Q
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
9.7 Labeling an electrode as positive or negative will not be assessed.
9.9 Calculations involving the Nernst equation
Electrochemical Cells Simulation/Animation: Animation of a galvanic cell undergoing a redox reaction and a volt meter is placed between the two half-cells to measure the cell potential. Animations of molecular-level movement at the cathode and anode are shown.
Electrochemical Virtual Lab: Select various metals as the anode or cathode, select the correct ionic solutions, and using a table of cell potentials predict and measure the voltage of the cell that you created. Description and background info are provided. Very helpful practice of how to set up a cell.
Electrochemical Cell Animation (2 min): simple, short animation of how electrons transfer from the anode to the cathode in a galvanic cell.
Standard Reduction Potentials Table (PDF): This is used in nearly every electrochem problem. Print a copy on a bright sheet of paper for use during class and at home. The AP exam will provide you with a table of reduction potentials or will give you specific values throughout the exam.
Solving for ΔG in a RedOx Reaction: Using the equation ΔG = -nFE°
How Does Electroplating Work? Short video explaining the process of electroplating.
Electrolysis of Water 1: (Tutor Vista) Follow the links listed on the left labeled "Electrolysis of Water", "Introduction to Electrolysis", "Application of Electrolysis", "Faraday's Second Law of Electrolysis", and "Faraday's First Law of Electrolysis".
Electrolysis of Water 2: (EduMedia) General explanation of how electrolysis of water works.
***Galvanic Cells aka Voltaic Cells (23 min) - Tyler DeWhitt explains how galvanic cells behave and how voltage is produced
***Introduction to Electrochemistry (16 min) - Tyler DeWhitt explains how redox reactions work in an electrochemical cell, the difference between galvanic and electrolytic cells, and standard reduction potentials
***Overview of Electrochemistry Basics (9 min) - Bozeman Science explains the general ideas behind how electrochemistry works *great overview*
Unit 5: Kinetics
Unit 5: Kinetics
Standards
5.1 Reaction Rates
5.2 Intro to Rate Law
5.3 Concentration Changes Over Time
5.4 Elementary Reactions
5.5 Collision Model
5.6 Reaction Energy Profile
5.7 Intro to Reaction Mechanisms
5.8 Reaction Mechanism and Rate Law
5.9 Steady-State Approximation
5.10 Multi-step Reaction Energy Profile
5.11 Catalysis
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
5.1 Calculate the rate of change (change in concentration over change in time)
5.1 Rate of reaction is affected by concentrations, temperature, surface area, catalysts, and other environmental factors
5.2 Determine the order of reaction
5.3 Using Integrated Rate Laws & Half-Life
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
5.6 Calculations involving the Arrhenius equation will not be assessed
5.8 Collection of data pertaining to detection of a reaction intermediate will not be assessed
Resources
Chemical Kinetics Overview: A playlist of four videos including reaction rate, rate laws, rate constants, overall order, integrated rate law, half-life, mechanisms, and more.
Bozeman Science Videos Kinetics (Playlist): 11 videos in one playlist for help on Kinetics
Unit 6: Thermodynamics
Unit 6: Thermodynamics
Standards
6.1 Endo/Exothermic Processes
6.2 Energy Diagrams
6.3 Heat Transfer and Thermal Equilibrium
6.4 Heat Capacity and Calorimetry (Specific Heat)
6.5 Energy of Phase Changes
6.6 Intro to Enthalpy of Reaction
6.7 Bond Enthalpies (Bond Energies)
6.8 Enthalpy of Formation
6.9 Hess's Law
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
6.4 Equation: q = mcΔT
6.8 Equation: ΔH°RXN = ΣΔHf°products - ΣΔHf°reactants
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
6.6 The technical distinctions between enthalpy and internal energy will not be assessed on the AP Exam.
6.9 State function will not be assessed, although the use of Hess's Law will be assessed.
Resources
Enthalpy, Entropy, & Gibb's Free Energy: Brief overview of each thermo topic.
How much heat is released? A video example of how to solve for enthalpy of reaction.
Hess's Law: Using Hess's Law to solve for ΔH of reaction
Calorimetry: Explanation and practice AP problems
Coffee Cup Calorimeter: Explanation of how a coffee cup calorimeter is set up
Specific Heat: Using q=mcΔT to solve thermo problems.
Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics Part II
Standards
9.1 Intro to Entropy
9.2 Absolute Entropy and Entropy Change
9.3 Gibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Favorability
9.4 Thermodynamic and Kinetic Control
9.5 Free Energy and Equilibrium (and 7.14 Free Energy of Dissolution)
9.6 Coupled Reactions
Resources
Enthalpy, Entropy, & Gibb's Free Energy: Brief overview of each thermo topic.
Using Gibb's Equation: Bozeman Science video on how to interpret Gibb's equation as the variables change.
Free Energy POGIL: A series of questions that relates enthalpy, entropy, and Gibb's free energy. Terms also used include: exothermic, endothermic, exergonic, endergonic, spontaneous, 2nd Law of Thermodynamics, and coupled processes.
Electrochemical Cells Simulation/Animation: Animation of a galvanic cell undergoing a redox reaction and a volt meter is placed between the two half-cells to measure the cell potential. Animations of molecular-level movement at the cathode and anode are shown.
Electrochemical Virtual Lab: Select various metals as the anode or cathode, select the correct ionic solutions, and using a table of cell potentials predict and measure the voltage of the cell that you created. Description and background info are provided. Very helpful practice of how to set up a cell.
Electrochemical Cell Animation (2 min): simple, short animation of how electrons transfer from the anode to the cathode in a galvanic cell.
Standard Reduction Potentials Table (PDF): This is used in nearly every electrochem problem. Print a copy on a bright sheet of paper for use during class and at home. The AP exam will provide you with a table of reduction potentials or will give you specific values throughout the exam.
Solving for ΔG in a RedOx Reaction: Using the equation ΔG = -nFE°
How Does Electroplating Work? Short video explaining the process of electroplating.
Electrolysis of Water 1: (Tutor Vista) Follow the links listed on the left labeled "Electrolysis of Water", "Introduction to Electrolysis", "Application of Electrolysis", "Faraday's Second Law of Electrolysis", and "Faraday's First Law of Electrolysis".
Electrolysis of Water 2: (EduMedia) General explanation of how electrolysis of water works.
Unit 7: Equilibrium
Unit 7: Equilibrium
Standards
7.1 Intro to Equilibrium
7.2 Direction of Reversible Reactions
7.3 Reaction Quotient and Equilibrium Constant
7.4 Calculating the Equilibrium Constant
7.5 Magnitude of Equilibrium Constant
7.6 Properties of the Equilibrium Constant
7.7 Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
7.8 Representations of Equilibrium
7.9 Intro to Le Chatelier's Principle
7.10 Reaction Quotient and Le Chatelier's Principle
7.11 Intro to Solubility Equilibria
7.12 Common-Ion Effect
7.13 pH and Solubility
7.14 Free Energy of Dissolution (Covered later during 9.5*)
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
7.6 Multiple Equilibria Rule
7.6 Coefficient Rule
7.6 Reciprocal Rule
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
7.3 Converting between Kc and Kp will not be assessed on the exam.
7.3 Equilibrium calculations on systems where a dissolved species is in equilibrium with that species in the gas phase.
7.13 Computations of solubility as a function of pH will not be assessed.
Resources
Practice Problem using Solubility (Ksp): Practice problem using an ICE table and calcium phosphate
Practice Problems #2 using Solubility (Ksp): Two practice problems (1) solving for Ksp and (2) solving for molarity when given Ksp.
Bozeman 15: Solutions: Discusses mixtures, solutions, chromatography, distillation, conductivity, enthalpy of formation of solutions, and calculating molarity.
Bozeman 70: Solubility: Discussed dissolution, equilibrium solubility constants Ksp, saturation, enthalpy/entropy during dissolution.
Equilibrium Review: A 1-hour video of AP-level practice problems explained on only equilibrium.
Using ICE Tables: How to set up an ICE table and a sample problem explained.
Equilibrium Practice Problems: Six problems explained.
Le Chatelier's Principle Explained Part 1 by Fuse (4 min) - Concentration and Pressure changes as stresses
Le Chatelier's Principle Explained Part 2 by Fuse (3 min) - Temperature as a stress
Free Energy and Equilibrium (7 min) - Bozeman Science
LAB: Applications of Le Chatelier's Principle: Handout with explanations
Unit 8: Acids and Bases
Unit 8: Acids and Bases
Standards
8.1 Intro to Acids and Bases
8.2 pH and pOH of Strong Acids and Bases
8.3 Weak Acid and Base Equilibria
8.4 Acid-Base Reactions and Buffers
8.5 Acid-Base Titrations
8.6 Molecular Structure of Acids and Bases
8.7 pH and pKa
8.8 Properties of Buffers
8.9 Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
8.10 Buffer Capacity
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
8.5 Computation of the concentration of each species present in the titration curve for polyprotic acids
8.9 Computation of the change in pH resulting from the addition of an acid or base to a buffer
8.9 Derivation of the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
Resources
AP Chem YouTube Review Unit 8 - 8.1 Introduction to Acids and Bases (48 min)
AP Chem YouTube Review Unit 8 - 8.2 pH and pOH of Strong Acids and Bases (43 min)
AP Chem YouTube Review Unit 8 - 8.3 Weak Acid and Base Equilibria (50 min)
Acid-Base Practice Problems: Bronsted-Lowry, Conjugate acid-base pairs, relative acid strengths, [H3O+] and [OH-], and pH problems
Calculating pH and pOH: Worksheet with answer key
Acids and Bases Overview: Covers every topics you could ever want (and some topics you will not want).
Qualitative Analysis of Various Ions: includes using ammonia or NaOH to identify unknown ions in solution like ammonium, zinc, iron, lead, copper, aluminum, and calcium.
Titration Curves: (11 mins) side-by-side comparison of four types of titration curves
Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics
Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics
Standards
9.1 Intro to Entropy
9.2 Absolute Entropy and Entropy Change
9.3 Gibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Favorability
9.4 Thermodynamic and Kinetic Control
9.5 Free Energy and Equilibrium (and 7.14 Free Energy of Dissolution)
9.6 Coupled Reactions
9.7 Galvanic (Voltaic) and Electrolytic Cells
9.8 Cell Potential and Free Energy
9.9 Cell Potential Under Nonstandard Conditions
9.10 Electrolysis and Faraday's Law
Skills NEEDED on the AP Exam
9.3 Table: G, H, S for favorability
9.9 Qualitative use of the Nernst equation: E = E° - (RT/nF) ln Q
Skills NOT on the AP Exam
9.7 Labeling an electrode as positive or negative will not be assessed.
9.9 Calculations involving the Nernst equation
Resources
Enthalpy, Entropy, & Gibb's Free Energy: Brief overview of each thermo topic.
Using Gibb's Equation: Bozeman Science video on how to interpret Gibb's equation as the variables change.
Free Energy POGIL: A series of questions that relates enthalpy, entropy, and Gibb's free energy. Terms also used include: exothermic, endothermic, exergonic, endergonic, spontaneous, 2nd Law of Thermodynamics, and coupled processes.
Electrochemical Cells Simulation/Animation: Animation of a galvanic cell undergoing a redox reaction and a volt meter is placed between the two half-cells to measure the cell potential. Animations of molecular-level movement at the cathode and anode are shown.
Electrochemical Virtual Lab: Select various metals as the anode or cathode, select the correct ionic solutions, and using a table of cell potentials predict and measure the voltage of the cell that you created. Description and background info are provided. Very helpful practice of how to set up a cell.
Electrochemical Cell Animation (2 min): simple, short animation of how electrons transfer from the anode to the cathode in a galvanic cell.
Standard Reduction Potentials Table (PDF): This is used in nearly every electrochem problem. Print a copy on a bright sheet of paper for use during class and at home. The AP exam will provide you with a table of reduction potentials or will give you specific values throughout the exam.
Solving for ΔG in a RedOx Reaction: Using the equation ΔG = -nFE°
How Does Electroplating Work? Short video explaining the process of electroplating.
Electrolysis of Water 1: (Tutor Vista) Follow the links listed on the left labeled "Electrolysis of Water", "Introduction to Electrolysis", "Application of Electrolysis", "Faraday's Second Law of Electrolysis", and "Faraday's First Law of Electrolysis".
Electrolysis of Water 2: (EduMedia) General explanation of how electrolysis of water works.
***Galvanic Cells aka Voltaic Cells (23 min) - Tyler DeWhitt explains how galvanic cells behave and how voltage is produced
***Introduction to Electrochemistry (16 min) - Tyler DeWhitt explains how redox reactions work in an electrochemical cell, the difference between galvanic and electrolytic cells, and standard reduction potentials
***Overview of Electrochemistry Basics (9 min) - Bozeman Science explains the general ideas behind how electrochemistry works *great overview*

Additional Resources
AP EXAM PREP
- 5 Steps to a 5 (McGraw-Hill) for long-term review ~$10
- Crash Course (REA) for short-term review ~$10
- AP Chemistry High-Yield Practice Questions (Sterling Test Prep) for practice questions ~$23
- Cracking the AP Chemistry Exam (Princeton Review) as a supplemental review book ~$12
- Barron’s AP Chemistry 8th Edition (Barron) as a supplemental review book ~$11
Released Exams with Video Explanations - Free Response Questions
AP EXAM OVERVIEW - 2024
AP EXAM OVERVIEW - 2024
Exam Information
Students MAY use a calculator on ALL parts of the exam this year!
PART 1: 50-60 MCQs approximately 90 minutes
PART 2: 7 FRQs (3 long, 10 points each; 4 short, 4 points each) approximately 105 minutes
Testing Information
Date: Monday, May __6_, 2024
Time to Arrive:
Time to Begin:
Time to Leave: Approximately 3:15pm
Location:
Things to Bring: Calculator, Pencils, Blue/Black Pens, Water, Snacks, Government ID
Things NOT to Bring: Study materials, scratch paper, reference sheets, leave cell phone in car
For More Information: https://apstudents.collegeboard.org/exam-calendar
AP CHEMISTRY CLASS RULES
Here you will find the class rules and guidelines for the course
APClassRules 2.doc
LAB SAFETY SHEET
